soil permeability test pdf|soil permeability formula : distribute Data related to the permeability of soil is necessary for calculating the amount of seepage through earthen dams or under sheet pile walls, the seepage rate from waste storage facilities .
web12 de fev. de 2024 · Een online casino Nederland zonder registratie zal nooit om je persoonlijke gegevens vragen. Je hoeft dus geen kopieën van documenten in te leveren, zoals je paspoort of ID kaart. Wordt dit wel gevraagd, dan heb je niet te maken met online gokken zonder registratie. Dus houd dit goed in de gaten.
{plog:ftitle_list}
webBest Welcome Bonus. The best welcome bonus in 2024 offers a generous match percentage, a high maximum bonus amount, and reasonable wagering requirements. For example, a casino might offer a 200% match bonus up to $1,000, meaning that if you deposit $500, you’ll receive an additional $1,000 in bonus funds to play with.
Oxygen Transmission Rate Test System vendor
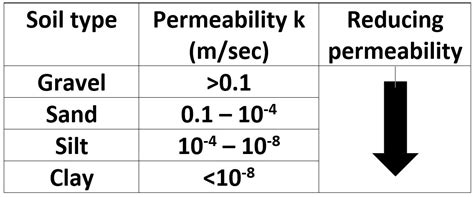
typical permeability values of soil
Report the test results in tabular form. Be sure to include: project E.A., date, sample number and any other pertinent information. Dry density and relative compaction (%) versus permeability and grain-size distribution can be included on attached graphs. . See moreThe entire system, including the porous stones and tubing, must be saturated prior to the test. This can be done by forcing water through the . See moreIn this test, water is forced, by a falling head pressure, through a soil specimen of known dimensions and the rate of flow is determined. This test is used to determine the drainage characteristics of relatively fine-grained soils and is usually performed on undisturbed . See more
typical permeability of soils
The specimen cannot be placed with the apparatus tipped on its side as the apparatus must be filled with water at all times. The placing procedure requires the following steps: Place soil ring and specimen with “O” ring, on bottom porous stone. Slide . See more
Permeability is one of the most important soil properties of interest to geotechnical engineering. Permeability influences the rate of settlement of a saturated soil under load. The design of .Data related to the permeability of soil is necessary for calculating the amount of seepage through earthen dams or under sheet pile walls, the seepage rate from waste storage facilities .
9.5 Measurement of soil permeability in the field . To measure soil permeability in the field, you can use one of the following tests: The visual evaluation of the permeability rate of soil horizons; A simple field test for estimating soil .The soil type and purpose of the test, accuracy required, and specimen type influence the selected test method. How is Soil Permeability Measured Soil Permeability tests take place under either constant head or falling head conditions: 3 Constant Head Test refers to an apparatus where the same relative elevation of the top of the water column .
Soil permeability is the quality of a soil enabling it to transmit air or water through the soil pores. Texture, structure, cracking, and the amount of organic matter influence the permeability. . Save as PDF Page ID 14681; Anna R. Schwyter & Karen L. Vaughan; University of Wyoming via UW Open Education Resources (OER) 6000 Broken Sound Parkway NW, Suite 300, Boca Raton, FL 33487-2742Lab Report-Permeability Test - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document describes the procedure for conducting a falling head permeability test to determine the coefficient of permeability (k) of a soil sample. It explains that the falling head test method is used for less permeable soils like silts and clays. Laboratory tests to establish basic mix and construction procedure for special experimental test section; results of 10 yr performance test are evaluated and modifications in mix design .
This permeability testing guidance document has been prepared to assist owners or operators of major facilities in preparing and executing a soil permeability testing program. It lays out acceptable soil sampling and permeability testing procedures, as well as what should be in a complete soil permeability testing report.SOIL CLASSIFICATION AND LABORATORY TESTING 5.0 GENERAL: WEIGHT VOLUME RELATIONSHIP In nature, soils are three-phase systems consisting of solid soil particles, water, and air (or gas). . The results of sieve analyses, plotted in the form of a gradation curve, are used to estimate soil permeability. The following tests shall be performed on .representative sample of the complete soil prior to the perme-ability test. Any particles larger than 19 mm (3⁄4 in.) shall be separated out by sieving (Method D 422). This oversize mate-rial shall not be used for the permeability test, but the percentage of . 1.1 This test method covers the determination of the coefficient of permeability by a constant-head method for the laminar flow of water through granular soils. The procedure is to establish representative values of the coefficient of permeability of granular soils that may occur in natural deposits as placed in embankments, or when used as base courses under pavements.
The falling head test measures the permeability at specific depths yielding a detailed permeability profile versus depth. Conversely, the pumping test provides an average permeability for the soil stratum. The measured permeability values lie within the typical ranges for sands and silty sands (e.g. [22], [21]). The permeability profiles from .The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, where as the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable discharge in a given time. For very fine-grained soil, capillarity permeability test is recommended. Principle of the ExperimentPermeability is defined as a capacity of soil to allow water passes through it i.e. quantity of flowing for a unit of soil surface under a pressure of 1 unit hydraulic gradient. Permeability is also known as hydraulic conductivity. Coefficient of permeability (k) is the flow velocity produced by hydraulic gradient of unity using the following6.6 Preparation of Specimen for Permeability Test: 6.6.1 Level the upper surface of the soil by placing the upper porous plate or screen in position and by rotating it gently back and forth. 6.6.2 Measure and record: the final height of specimen, H1 − H2, by measuring the depth, H2, from the upper surface of the perforated top plate employed .
permeability of soil governs the type of soil to be used. 0.4 This Standard ( Part 17) covers both constant head and falling head tests as used for most of the soil. The laboratory determination of permeability of granular soil by constant head method is covered in separate part ( Part 36 ).
representative sample of the complete soil prior to the perme-ability test. Any particles larger than 19 mm (3⁄4 in.) shall be separated out by sieving (Method D 422). This oversize mate-rial shall not be used for the permeability test, but the percentage of .tests, see Reference 2, Soil Testing for Engineers, by Lambe, Reference 3, The Measurement of Soil Properties in the Triaxial Test, by Bishop and Henkel, and other criteria sources. 1.3 TEST SELECTION FOR DESIGN. Standard (ASTM) or suggested test procedures, variations that may be appropriate, and type and size of sample are included in Tables
Permeability Test Lab Report - Free download as Word Doc (.doc), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. permeability Test Lab Report is an edition which help to engineering students to get a set of knowledge. Manual of soil laboratory testing. Volume 2, Permeability, shear strength and compressibility tests . 8 Scope, equipment and laboratory practice -- 9 Preparation of test specimens -- 10 Permeability and erodibility tests -- 11 California Bearing Ratio -- 12 Direct shear tests -- 13 Undrained compression tests -- 14 Oedometer consolidation .The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable discharge in a given time. For very fine-grained soil, capillarity permeability test is recommended. Usually, permeability of soils is determined by two methods: The constant head permeability test is usually preferred for sandy soils and the variable head permeability test for silty and clayey soils. A separate constant head method for granular soils has been recommended by Indian Standards (IS: 2720 – Part 36, 1975).
This document describes the procedure for conducting a constant head permeability test to determine the coefficient of permeability of soils according to Indian standards. It provides 3 key points: 1. The constant head permeability test is used to measure the permeability of coarse-grained soils that allow reasonable water flow over time. It involves setting up a constant head .Geotechnical investigation and testing — Laboratory testing of soil — Part 11: Permeability tests 1 Scope This document specifies methods for the laboratory determination of the water flow characteristics in soil. This document is applicable to the laboratory determination of the coefficient of permeability of soil
soil permeability test procedure
PERMEABILITY TEST 1. Objective The rate of flow of water, under laminar flow conditions, through a unit cross sectional are of soil mass, under unit hydraulic gradient, is defined as coefficient of permeability. Permeability of the soil governs the magnitude of excess pore water pressure built-up
soil permeability formula
The findings indicate that the triaxial test demonstrates the highest permeability, whereas the falling head test exhibits the lowest. . Determination of permeability of a soil-Constant head method using a flexible wall permeameter. Google Scholar. . (PDF). EPA 530-F-97-002 Fact Sheet Revised December 2001. Google Scholar.Manual of Soil Laboratory Testing—Volume 2: Permeability, Shear Strength and Compressibility Tests . Based on: Manual of Soil Laboratory Testing—Volume 2: Permeability, Shear Strength and Compressibility Tests, 3rd Edition. Head K. H. and Epps R. J. Whittles Publishing, Caithness, 2011, £110.00, hardback, 499pp., ISBN: 978-1904445-69-2 .FIELD MANUAL 110 Table 17-1.—A glossary of abbreviations and definitions used in permeability calculations K = Coefficient of permeability in feet (meters) per year under a unit gradient. Q = Steady flow into the well in ft3/sec [m3/sec]. H = The effective head of water in the well in feet (m). For packer tests, determining the effective head is defined
Electrolytic Sensor Method vendor
Flex Durability Tester factory vendor
Atlético Mineiro next match. Atlético Mineiro will play the nex.
soil permeability test pdf|soil permeability formula